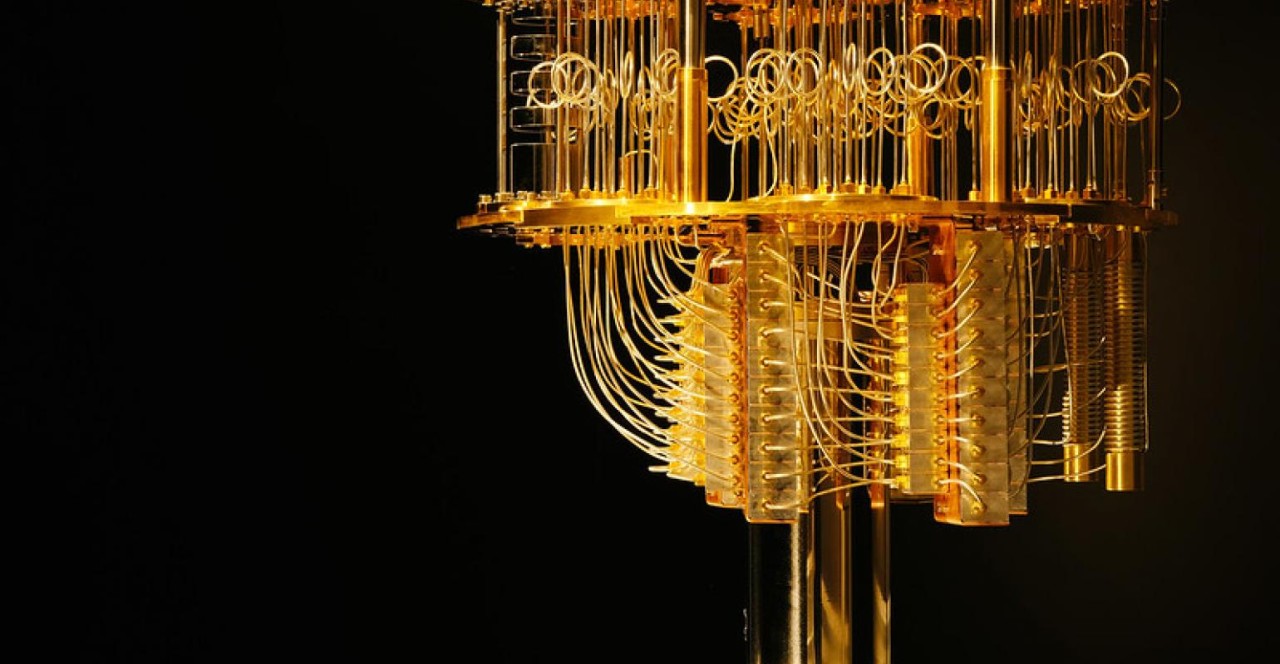
As technology continues to evolve at a rapid pace, quantum computing stands out as one of the most revolutionary advancements on the horizon. Unlike classical computers, which process information using binary bits, quantum computers leverage the principles of quantum mechanics to perform computations in fundamentally different ways. This article explores the fascinating world of quantum computing, its potential applications, and the challenges facing its development.
1. What is Quantum Computing?
Quantum computing is a type of computing that harnesses the unique properties of quantum mechanics to process information in ways that classical computers cannot. Key concepts in quantum computing include:
- Qubits: Unlike classical bits, which are either 0 or 1, qubits can exist in multiple states simultaneously, thanks to a property known as superposition. This allows quantum computers to perform many calculations at once.
- Entanglement: Quantum entanglement is a phenomenon where qubits become interconnected such that the state of one qubit instantly influences the state of another, regardless of distance. This property enables quantum computers to solve complex problems more efficiently.
- Quantum Gates: Quantum gates manipulate qubits in a quantum circuit, analogous to classical logic gates but with the ability to process information in superposition and entanglement.
- Quantum Speedup: Quantum computers can potentially solve certain types of problems exponentially faster than classical computers by leveraging the principles of superposition and entanglement.
2. Potential Applications of Quantum Computing
Quantum computing has the potential to transform various fields and industries by solving problems that are currently intractable for classical computers:
- Cryptography: Quantum computers could break existing cryptographic algorithms by efficiently solving problems that are currently considered secure. This has significant implications for data security and privacy, leading to the development of quantum-resistant encryption methods.
- Drug Discovery: Quantum computing could revolutionize drug discovery by simulating molecular interactions with unprecedented accuracy. This could accelerate the development of new pharmaceuticals and personalized medicine.
- Optimization Problems: Quantum computers can tackle complex optimization problems in logistics, finance, and supply chain management. By exploring multiple solutions simultaneously, quantum computers can find optimal or near-optimal solutions more efficiently.
- Material Science: Quantum computing could advance the understanding and design of new materials with tailored properties. This has applications in fields such as energy storage, electronics, and manufacturing.
- Artificial Intelligence: Quantum computing could enhance machine learning algorithms by providing faster processing capabilities and enabling the exploration of larger datasets. This could lead to more advanced AI models and applications.
3. Current State of Quantum Computing
The field of quantum computing is still in its early stages, with significant progress being made but many challenges remaining. Key developments include:
- Quantum Hardware: Researchers are developing various types of quantum hardware, including superconducting qubits, trapped ions, and topological qubits. Each approach has its own advantages and challenges in terms of stability, scalability, and error rates.
- Quantum Supremacy: In October 2019, Google claimed to have achieved quantum supremacy by demonstrating that its quantum computer, Sycamore, could perform a specific task faster than the world’s most powerful supercomputer. This milestone marked a significant step forward but is just the beginning of practical quantum computing.
- Quantum Algorithms: Scientists are developing quantum algorithms designed to take advantage of quantum computing’s unique capabilities. These algorithms aim to solve problems more efficiently than classical algorithms and are crucial for realizing the potential of quantum computing.
- Commercialization Efforts: Companies such as IBM, Google, and Microsoft are investing heavily in quantum computing research and development. Efforts are underway to build practical quantum computers and develop quantum cloud services for businesses and researchers.
4. Challenges and Considerations
Despite its potential, quantum computing faces several challenges that must be addressed:
- Error Rates: Quantum computers are highly susceptible to errors due to decoherence and noise. Developing error correction techniques and improving qubit stability are critical for building reliable quantum systems.
- Scalability: Scaling up quantum computers to handle more qubits and larger problems is a significant challenge. Researchers are exploring various approaches to increase the number of qubits and improve connectivity between them.
- Resource Requirements: Quantum computers require specialized hardware and operating conditions, such as extremely low temperatures. The resources and infrastructure needed to maintain and operate quantum systems can be substantial.
- Algorithm Development: Developing quantum algorithms that can solve practical problems is a complex task. Researchers are working to identify problems that can benefit from quantum computing and design algorithms that can leverage quantum advantages.
5. The Future of Quantum Computing
Looking ahead, several trends and developments are likely to shape the future of quantum computing:
- Integration with Classical Systems: Quantum computing is expected to complement classical computing rather than replace it. Hybrid systems that combine quantum and classical computing will be developed to tackle problems more efficiently.
- Quantum Networking: Quantum networking aims to create secure communication channels using quantum entanglement. This could lead to the development of quantum internet, enabling secure data transmission and new types of communication protocols.
- Government and Industry Support: Governments and industries worldwide are investing in quantum computing research and development. Public-private partnerships and international collaborations will drive innovation and accelerate progress in the field.
- Ethical and Societal Implications: The rise of quantum computing will have ethical and societal implications, particularly in areas such as data security and privacy. Addressing these concerns will be important for ensuring the responsible development and deployment of quantum technology.
6. Conclusion
Quantum computing represents a transformative leap in computational technology, with the potential to revolutionize various fields and solve complex problems that are currently beyond the reach of classical computers. As research and development efforts continue, addressing the challenges and embracing the opportunities presented by quantum computing will be crucial for realizing its full potential. By staying informed about the latest advancements and preparing for the impact of quantum technology, businesses and individuals can position themselves to benefit from this groundbreaking innovation.